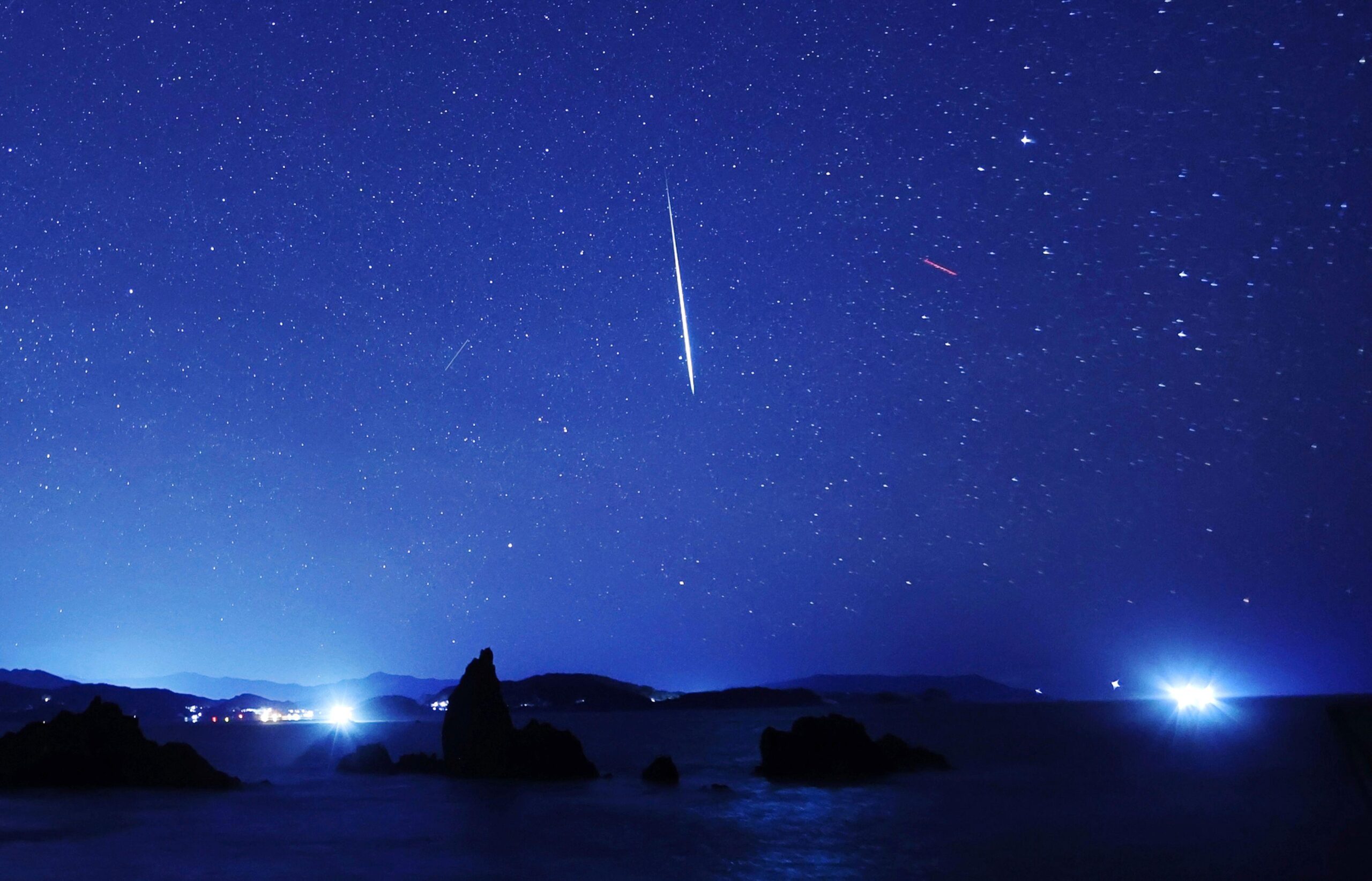
If you’ve ever stepped outside on a cold January night hoping to catch a dramatic moonrise or a meteor streak cutting across the sky, you’re not alone.
January is one of the most active months of the year for night-sky watching. It brings the Wolf Moon, the year’s first full Moon, which can appear especially bright when it coincides with a supermoon, along with the Quadrantid meteor shower, one of the strongest annual meteor events known for its bright, fast-moving streaks.
Together, these events make January a prime time for skywatching—but the experience isn’t equal everywhere. Cloud cover, humidity, elevation, and light pollution can mean the difference between a crisp supermoon or meteor streak and a washed-out gray sky where nothing stands out.
To measure those differences, our odds team analyzed January night-sky conditions across all 50 states using 10 equally weighted metrics covering sky darkness, weather, air clarity, astronomical geometry, and real-world observations, assigning each state an implied probability and its equivalent moneyline odds to create the January Night-Sky Visibility Index.
The index estimates how likely someone in each U.S. state is to experience clear, high-quality views of January’s biggest night-sky events, from the Wolf Moon Supermoon to Quadrantid meteors and general winter stargazing.
Key Findings
- Alaska ranks No. 1 overall, with the nation’s darkest skies (99.22% estimated dark-sky coverage) and the longest stretches of true nighttime (11.96 hours per night).
- Florida ranks last, where low elevation, high humidity, and frequent cloud cover make January skywatching the most challenging.
- The Mountain West dominates, with Colorado, Wyoming, Montana, New Mexico, Nevada, and Utah all landing in the top 10 thanks to elevation and widespread darkness.
- The bottom of the list is concentrated in humid or heavily light-polluted states, where cloudier skies and urban glow stack the deck against clear viewing.
- Most states fall into a broad middle tier, where decent darkness and night length exist, but clear viewing depends heavily on timing, weather, and location.
Top 10 U.S. States for January Night-Sky Viewing
1) Alaska
Implied Probability: 27.42% | Moneyline Odds: +265
- Nearly the entire state remains naturally dark (estimated dark-sky coverage: 99.22% of land area)
- Almost no artificial glow competing with stars (night-sky brightness: 0.01 mcd/m²)
- The longest true nights in the U.S. (average fully dark hours: 11.96 hr/night)
Put together, Alaska offers unmatched darkness and time, with long winter nights and minimal artificial light making stars, meteors, and moonlight stand out clearly and effortlessly.
2) Colorado
Implied Probability: 25.85% | Moneyline Odds: +287
- High altitude brings you closer to the sky (average elevation: 6,800 ft)
- Most of the state avoids heavy light pollution (estimated dark-sky coverage: 93.52%)
- Long winter nights support extended viewing (average fully dark hours: 11.07 hr/night)
Together, Colorado’s elevation and widespread darkness sharpen the night sky, allowing stars and meteors to appear brighter and clearer even during cold winter nights.
3) Wyoming
Implied Probability: 24.55% | Moneyline Odds: +307
- Vast areas remain naturally dark (estimated dark-sky coverage: 98.72%)
- Extremely clean winter air (PM2.5: 3.13 µg/m³)
- Very low artificial sky glow (night-sky brightness: 0.03 mcd/m²)
As a result, Wyoming delivers one of the cleanest and least obstructed night skies in the country, where faint stars and subtle meteor trails are easier to spot.
4) Montana
Implied Probability: 24.02% | Moneyline Odds: +316
- Most of the land stays free from light pollution (estimated dark-sky coverage: 98.54%)
- Minimal artificial brightness statewide (0.03 mcd/m²)
- Extra-long January nights (average fully dark hours: 11.36 hr/night)
Because of its long, dark winter nights and minimal light interference, Montana gives observers more time and flexibility to enjoy celestial events without rushing.
5) New Mexico
Implied Probability: 23.79% | Moneyline Odds: +320
- Very clean air with little haze to blur stars or meteors (PM2.5: 5.44 µg/m³)
- Large portions of land remain naturally dark (estimated dark-sky coverage: 94.76%)
- The Moon climbs well above the horizon (Moon height after rise: 22.31° above the horizon)
Taken together, New Mexico’s clean air, darkness, and favorable Moon position create stable, high-contrast skies that make both lunar detail and meteors easy to enjoy.
6) Nevada
Implied Probability: 22.73% | Moneyline Odds: +340
- Wide desert areas stay free from city glow (estimated dark-sky coverage: 96.42%)
- Low artificial brightness across the state (0.07 mcd/m²)
- Meteors appear high and unobstructed (30.35° above the horizon)
Combined with open horizons, Nevada’s desert darkness allows meteors and moonlit landscapes to stand out clearly with very little visual interference.
7) Maine
Implied Probability: 21.80% | Moneyline Odds: +359
- A large share of land remains naturally dark (estimated dark-sky coverage: 94.14%)
- Meteors rise high overhead (35.79° above the horizon)
- Long winter nights support extended viewing (average fully dark hours: 11.28 hr/night)
Even without high elevation, Maine’s darkness and favorable meteor angles combine to make it the most reliable January night-sky destination in the Northeast.
8) California
Implied Probability: 20.63% | Moneyline Odds: +385
- More reported fireball sightings than any other state (9,340 reports in five years)
- Large inland areas still remain naturally dark (estimated dark-sky coverage: 79.13%)
- Moderate elevation improves inland visibility (2,900 ft average)
While coastal cities are bright, California’s deserts and mountain regions reward those who travel inland with frequent fireball activity and strong night-sky views.
9) Arizona
Implied Probability: 20.16% | Moneyline Odds: +396
- Fewer clouds blocking the sky (average January cloud cover: 46.53%)
- Most of the state remains naturally dark (estimated dark-sky coverage: 92.9%)
- The Moon climbs high for clearer views (22.64° above the horizon)
Thanks to dry air and low cloud cover, Arizona delivers consistently clear nights, making it one of the most dependable states for January skywatching.
10) Utah
Implied Probability: 19.48% | Moneyline Odds: +413
- Strong statewide darkness (estimated dark-sky coverage: 95.4%)
- High elevation supports clearer skies (average elevation: 6,100 ft)
- Long winter nights allow extended viewing (average fully dark hours: 11.11 hr/night)
When conditions line up, Utah’s best locations offer world-class views, especially in desert and park regions where elevation and darkness work together.
Bottom 10 U.S. States for January Night-Sky Viewing
41) Kentucky
Implied Probability: 9.46% | Moneyline Odds: +957
- High winter humidity can add haze and soften the sky (average January humidity: 76.25%)
- Cloudy January weather blocks clear viewing nights (average January cloud cover: 76.32%)
- Lower elevation means you’re looking through more atmosphere (avg. elevation: 750 ft)
Put together, Kentucky’s humid, cloud-heavy winters and lower elevation make it harder to get sharp, consistently clear night-sky views.
42) Michigan
Implied Probability: 8.88% | Moneyline Odds: +1026
- More artificial light and light pollution washing out stars (estimated night-sky brightness: 0.54 mcd/m²)
- High winter humidity can blur faint stars and meteors (average January humidity: 82.07%)
- Very cloudy winter skies limit viewing windows (average January cloud cover: 90.19%)
Overall, Michigan’s skywatching challenges come from cloud cover first, with humid air and noticeable light pollution further reducing how crisp the sky looks.
43) Louisiana
Implied Probability: 8.39% | Moneyline Odds: +1092
- Very low elevation makes the sky less crisp (avg. elevation: 100 ft)
- Humid air can dull contrast and detail (average January humidity: 71.55%)
- Meteors tend to appear lower in the sky (meteor radiant height: 22.58° above the horizon)
Together, Louisiana’s low elevation and moisture-heavy air make the night sky look less sharp, and lower meteor angles make quick streaks easier to miss.
44) Rhode Island
Implied Probability: 8.17% | Moneyline Odds: +1124
- Very high artificial light and light pollution (estimated night-sky brightness: 1.71 mcd/m²)
- Almost no naturally dark land to escape city glow (estimated dark-sky coverage: 2.34% of land area)
- Low elevation adds to a “thicker air” view (avg. elevation: 200 ft)
As a result, Rhode Island has very few true dark-sky options, and the combination of heavy light pollution and low elevation makes stars look washed out most nights.
45) Maryland
Implied Probability: 7.09% | Moneyline Odds: +1310
- Moist winter air can soften visibility (average January humidity: 71.05%)
- Extremely high artificial light and light pollution (estimated night-sky brightness: 1.97 mcd/m²)
- Lower elevation reduces that “clear mountain sky” effect (avg. elevation: 350 ft)
In Maryland, humidity plus intense light pollution makes it tough for stars and meteors to stand out, especially outside a few limited darker pockets.
46) Ohio
Implied Probability: 6.51% | Moneyline Odds: +1436
- Cloudy winter skies reduce the number of usable nights (average January cloud cover: 81.96%)
- High artificial light and light pollution in many areas (estimated night-sky brightness: 1.16 mcd/m²)
- Limited naturally dark land statewide (estimated dark-sky coverage: 26.26% of land area)
Taken together, Ohio’s cloud cover, widespread artificial lighting, and limited dark land make strong night-sky viewing far less reliable than in higher-ranked states.
47) Indiana
Implied Probability: 5.80% | Moneyline Odds: +1624
- High humidity can create haze and reduce sharpness (average January humidity: 78.48%)
- Cloud-heavy winter nights limit viewing windows (average January cloud cover: 80.44%)
- Below-average naturally dark land (estimated dark-sky coverage: 35.48% of land area)
Overall, Indiana’s winter skies are often hazy and clouded over, and fewer naturally dark areas means even clear nights don’t always deliver strong star visibility.
48) New Jersey
Implied Probability: 5.51% | Moneyline Odds: +1714
- Low elevation limits natural clarity (avg. elevation: 250 ft)
- Almost no naturally dark land (estimated dark-sky coverage: 0.9% of land area)
- Extremely high artificial light and light pollution (estimated night-sky brightness: 2.53 mcd/m²)
In practice, New Jersey is one of the hardest states for night-sky viewing because true dark locations are rare and artificial light overwhelms the sky in most areas.
49) Delaware
Implied Probability: 5.48% | Moneyline Odds: +1725
- Very low elevation reduces sky clarity (avg. elevation: 60 ft)
- Lowest dark-sky availability in the entire table (estimated dark-sky coverage: 0.4% of land area)
- Very high artificial light and light pollution (estimated night-sky brightness: 1.50 mcd/m²)
Delaware ranks near the bottom because there’s almost nowhere to find naturally dark skies, and low elevation plus heavy light pollution further washes out what you can see.
50) Florida
Implied Probability: 4.03% | Moneyline Odds: +2381
- Very low elevation makes clear, crisp skies harder to get (avg. elevation: 100 ft)
- High humidity often adds haze (average January humidity: 75.93%)
- Cloudy winter nights block visibility (average January cloud cover: 72.66%)
Overall, Florida’s low elevation and moisture-heavy winter air—paired with frequent cloud cover—make it the toughest state in the table for consistent January night-sky viewing.
What About the Middle States?
Most U.S. states fall somewhere between the extremes. These mid-ranked states don’t have the overwhelming advantages of the top tier, but they also avoid the consistent obstacles seen at the bottom.
Take Missouri as a good example. The state has a decent amount of naturally dark land (estimated dark-sky coverage: 81.68%) and respectable winter night length (average fully dark hours: 11.05 hr/night), which gives observers enough time to watch the sky. However, cloud cover (70.53%) and moist winter air (75.04% humidity) often get in the way, so great viewing depends heavily on timing.
In short, mid-tier states can still deliver memorable night-sky experiences — especially on clear, well-timed nights and away from city lights — but they tend to lack the consistency and built-in advantages that define the top performers.
Curious where your state ranks? Explore the full January Night-Sky Visibility Index to see how all 50 U.S. states compare for sky clarity, darkness, and overall viewing conditions this January.
If analyzing odds and probabilities fascinates you beyond the Supermoon, take a look at Fliff Promo Code — a social sportsbook where you can test your instincts using virtual coins instead of real wagers.
Ideal Conditions for Seeing January Night-Sky Events Clearly
A clear night helps, but it is not the whole story. In January, the best night-sky views come down to darkness, dry air, timing, and location. Based on guidance from NASA, major observatories, and stargazing best practices, these are the conditions that give you the strongest chance of seeing and photographing January’s celestial events clearly.
- Time it around moonrise and moonset: The Supermoon looks largest and most dramatic when it is low on the horizon, near moonrise or moonset. This is when the moon illusion is strongest and foreground objects such as mountains, trees, or buildings add scale and visual impact. For meteor showers, later night and pre-dawn hours often offer darker skies and better contrast.
- Look for long stretches of true darkness: January offers some of the longest fully dark nights of the year, especially in northern states. More hours of complete darkness, with no twilight glow, mean more uninterrupted time to watch meteors and observe lunar detail.
- Seek dry, stable air: Low humidity is critical. Dry air scatters less light, making stars sharper and the Moon’s surface details clearer. Higher elevations also help by reducing atmospheric thickness and haze, which is why mountain and desert regions consistently perform well in winter.
- Avoid clouds, even thin ones: High cloud cover is one of the biggest obstacles to January skywatching. Even thin clouds can wash out stars and meteors or soften the Moon’s contrast. Checking short-term cloud forecasts is just as important as knowing when the event peaks.
- Get away from light pollution: Artificial light dulls contrast and overwhelms faint details. Rural areas, deserts, national parks, and open plains provide darker skies where meteors stand out and the Moon appears more defined. Even driving 20 to 30 minutes away from city centers can dramatically improve visibility.
- Choose a wide, open horizon: An unobstructed view, especially to the east or west, helps with moonrise, moonset, and low-angle meteor streaks. Open fields, desert overlooks, lakefronts, and elevated viewpoints work particularly well.
- Stabilize your camera or yourself: Cold January nights make camera shake more likely. Use a tripod or stable surface, and keep exposures short for the Moon to preserve detail. For meteors, longer exposures and patience increase your chances of catching a streak.
Methodology: How the ranking was calculated
To estimate how favorable each U.S. state is for seeing a supermoon and meteor activity in January, we analyzed a balanced mix of 10 equally weighted factors. Together, these metrics capture sky darkness, weather conditions, air clarity, astronomical geometry, and real-world observations.
The 10 metrics used
- Reported fireball sightings (past 5 years)
Real-world meteor reports, used as a proxy for how often bright meteors are actually observed.
Source: American Meteor Society (AMS) – eyewitness meteor and fireball reports across the U.S. - January air pollution (PM2.5)
Fine-particle pollution levels that reduce atmospheric transparency and make the night sky appear hazy.
Source: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) – nationwide outdoor air quality monitoring data. - Average January humidity (%)
Higher humidity scatters light and worsens sky clarity.
Source: Open-Meteo – historical weather data including humidity and cloud cover averages. - Average January cloud cover (%)
Cloudier skies reduce the chances of seeing celestial events.
Source: Open-Meteo – historical weather data including humidity and cloud cover averages. - Estimated artificial night-sky brightness (statewide, mcd/m²)
How bright the night sky is from human-made lighting across each state.
Source: World Atlas of Artificial Night Sky Brightness (2015), published in Science Advances (Falchi et al.), combined with U.S. Census state boundary data. - Estimated dark-sky coverage (Bortle 1–3, % of land area)
The share of land with naturally dark skies and minimal light pollution.
Source: World Atlas of Artificial Night Sky Brightness (2015), published in Science Advances (Falchi et al.), combined with U.S. Census state boundary data. - Average meteor radiant height above the horizon (degrees)
Higher radiant positions generally improve meteor visibility.
Source: Calculated using standard astronomical methods (Astropy), based on the Quadrantid meteor shower’s radiant location from In-The-Sky.org. - Moon height about two hours after moonrise (degrees)
Lower moon height means less moonlight glare during peak viewing hours.
Source: Skyfield astronomy library using NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) lunar ephemeris data. - Average elevation (feet)
Higher elevations usually offer thinner air and clearer viewing conditions.
Source: State elevation data compiled from Statista and U.S. geographic datasets. - Average hours of full astronomical darkness (January 2026)
The amount of time the sky is completely dark, with no twilight interference.
Source: Sunrise-Sunset.org API and U.S. Naval Observatory definitions of astronomical twilight.
How the final odds were produced
Our odds experts factored in all 10 of the above metrics, weighting each equally, to produce the implied probabilities and American odds for each U.S. state—highlighting where people have the best chance of viewing the supermoon and other night-sky events in January.
Note: These rankings are based on historical data, statewide averages, and modeled estimates. Individual viewing conditions may vary by location and by night.